
DES was later discontinued because of its short length and other security issues, although it is still regarded as a pioneer encryption standard. Initially, sensitive, private information was protected using a 56-bit symmetric key algorithm. Several encryption standard protocols that utilise block ciphers are: 1. The majority of contemporary cipher suites are based on block ciphers.
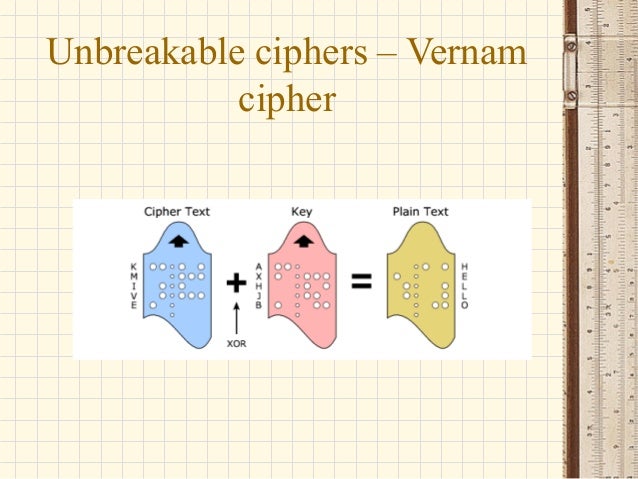
Vernam cipher series#
A series of XORs between blocks of plaintext and corresponding blocks of ciphertext can be used to represent the CTR encryption process. The process of encrypting data is performed by XORing the plaintext with a series of pseudorandom values that are each created from the ciphertext using a feedback function data is encrypted. Counter Mode (CTR)ĬTR mode uses a block chaining mode of encryption as a building block. It uses a feedback mechanism however, in OFB mode, the preceding block of ciphertext is XORed with the plaintext after encryption rather than prior to encryption. In certain ways, CBC and OFB modes are comparable and can be used with any block cipher. In CFB mode, the previous ciphertext block is encrypted, and the output is XORed with the current plaintext block to create the current ciphertext block.
Vernam cipher generator#
A block cipher is a part of the random number generator used by CFB. It is occasionally important to quickly encrypt and send plaintext values, one at a time, as opposed to CBC mode, which encrypts a predetermined number of bits of plaintext at a time. For example, Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security uses CBC mode in order to encrypt data which is transferred over the internet. Numerous security applications used CBC mode. Before using the cipher algorithm to encrypt the data, each block of plaintext is XORed (exclusive OR) with the block of ciphertext that came before it. This is done to ensure that every block of the ciphertext depends on every other block that came before it. A ciphertext generated by the symmetric algorithm depends on all plaintext block processed in the data stream before it. When using CBC mode to encrypt data, each block of plaintext is combined with the ciphertext that came before it. Only 8 bytes of the key are used when the plaintext block is only 8 bytes long, and all 100 bytes of the key are utilised when the plaintext block is 100 bytes long. Each block of plaintext is encrypted separately from every other block. Using the cipher's key and substitution alphabet, each plaintext symbol, such as a character from the plaintext alphabet, is transformed into a ciphertext symbol. It does not introduce any randomness to the key stream, and it is the only mode we can use to encrypt a single-bit stream. It is the most straightforward block cipher operating mode.
Vernam cipher code#
Electronic Codebook ModeĮlectronically code message in plaintext form is dine in ECB mode. These modes serve as a block cipher's general procedures principles. There are various modes of operation of a block cipher: This algorithm uses the public key to encrypt plaintext and a private key to decrypt the ciphertext.

Popular variations of the block cipher algorithm include the Data Encryption Standard (DES), TripleDES, and the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).The length of the output and input are identical. It uses the same key during decryption to change the cyphertext back to the original plaintext.

During encryption, it converts text input into cyphertext using the shared key. Since the block's size is fixed, padding is not necessary. With the help of the shared secret key, a block cipher encrypts and decrypts its input one block rather than one bit at a time. As a result, the lengthy message is broken up into a number of sequential message blocks, and the cipher operates on these blocks one at a time. Typically, a message's size exceeds a block's size. It uses the same key to encrypt both the plaintext, and the ciphertext.Ī block cipher processes the data blocks of fixed size. During encryption, we used plaintext and ciphertext is the resultant encrypted text. What is Block Cipher?Ī block cipher is a symmetric cryptographic technique which we used to encrypt a fixed-size data block using a shared, secret key. In this article, we will discuss the characteristics of block ciphers and stream ciphers and how they differ from one another. Next → ← prev Difference Between Block Cipher and Stream Cipherīlock cipher and stream cipher are members of the family of symmetric key ciphers, essentially encryption techniques used for directly transforming the plaintext into ciphertext.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
